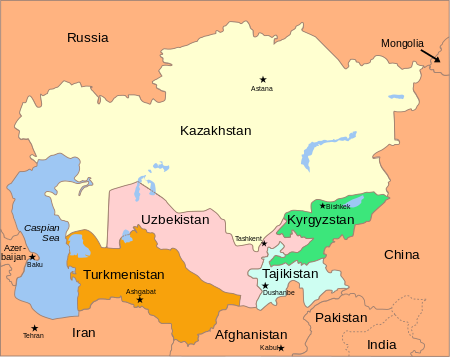
If you want to leave Kazakhstan, learn English. If you want to stay, learn Chinese.
What started as a joke in business and government circles in Astana and Almaty has taken on a serious tone as China’s economic, military, and political clout in Central Asia has increased. In the nineteenth century, China watched from the sidelines as Russian and British explorers, envoys, and spies wandered around its western provinces and Tibet, mapping trade routes, building alliances with local leaders, and hatching plots. The Chinese empire, weakened by internal discord and rebellion, could not play in the so-called Great Game. By the end of the twentieth century, the roles were, if not reversed, at least re-balanced, with China vying with Russia and the United States in a new Great Game. Hungry for oil, gas, and natural resources, China has invested heavily in Kazakhstan’s energy sector. It built the pipeline to carry oil from the Caspian Sea east to Xinjiang, and is financing construction of a gas pipeline and a 1,700-mile stretch of highway to connect China with Europe. Russia, Europe, and the United States support pipelines running west to the Black Sea and Turkey. For now, there’s plenty of oil to flow both ways, but the supply will not last forever. Analysts worry about population pressures: if its cities cannot accommodate more people, will China look west to the sparsely populated steppe?
Postcards from Stanland: Journeys in Central Asia (Ohio University Press, 2016) is available from Amazon, Barnes & Noble, Books-a-Million and other online retailers. Read excerpts at www.davidhmould.com (Travel Blogs) or Facebook /PostcardsFromStanland/ or view readings and interviews on YouTube
The end of the Soviet Union briefly revived the dream of the Uighurs of Xinjiang of uniting with their fellow Muslims in a Greater Turkestan or caliphate. China leaned heavily on Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan to restrict Uighur political activity and settled the border disputes that had plagued Chinese-Soviet relations. China has reduced the demographic power of the Uighurs by resettling Han Chinese in Xinjiang. With oil from Kazakhstan and gas from Turkmenistan, China no longer has to rely on sea routes that can be disrupted by the United States. China brought the Central Asian republics into the Shanghai Cooperation Organization and exploited new export markets.
Russia has long-standing economic ties with Kazakhstan. It’s also the economic magnet for thousands of migrant workers from Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, the two poorest countries in the region. Remittances from migrant workers in Russia account for about 29 percent of Kyrgyzstan’s GDP and 47 percent of Tajikistan’s. Russia provides aid and loans and maintains military bases in both countries. With the withdrawal of NATO forces from Afghanistan and the handover of the Manas air base in Bishkek, the United States no longer has a significant military presence in Central Asia, but its economic interests, particularly in Kazakhstan’s oil, gas, and mining sectors and in banking, make it the other major player. Iran and Turkey are also in the game, although only Turkey has so far invested heavily in the Central Asian economies and sought influence through education and social programs.
What happens in Central Asia as China, Russia, the United States, Turkey, and Iran—and possibly India, making a late entry to the game—compete will affect the world balance of economic and political power. As the journalist Ahmed Rashid, author of two books on Central Asia, remarks: “One of the great dangers for the U.S. and other Western powers will be continuing ignorance and neglect of what is happening there.”